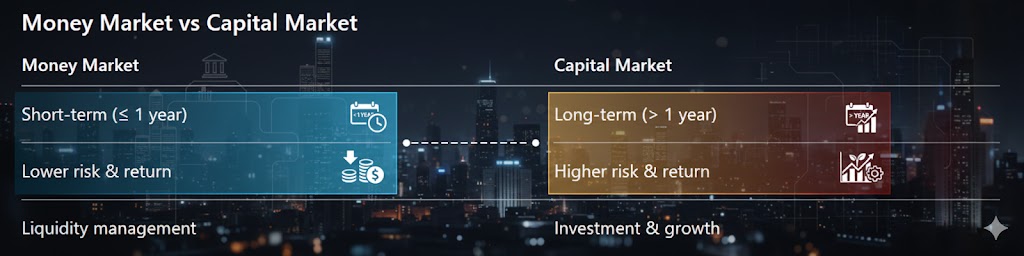
Money Market is a segment of the financial market where short-term funds are borrowed and lent, usually for periods of less than one year. It is mainly used to manage liquidity and meet short-term financing needs, rather than for long-term investment.
Key characteristics
- Short maturity: Overnight to under 1 year
- Low risk & high liquidity
- Large transaction sizes
- Lower returns compared to capital markets

Main participants
- Central banks
- Commercial banks
- Financial institutions
- Corporations
- Governments
Common money market instruments
- Treasury Bills (T-Bills): Short-term government securities
- Commercial Paper (CP): Unsecured short-term corporate debt
- Certificates of Deposit (CDs): Time deposits issued by banks
- Repurchase Agreements (Repos): Short-term borrowing using securities as collateral
- Interbank loans: Loans between banks
Functions of the money market
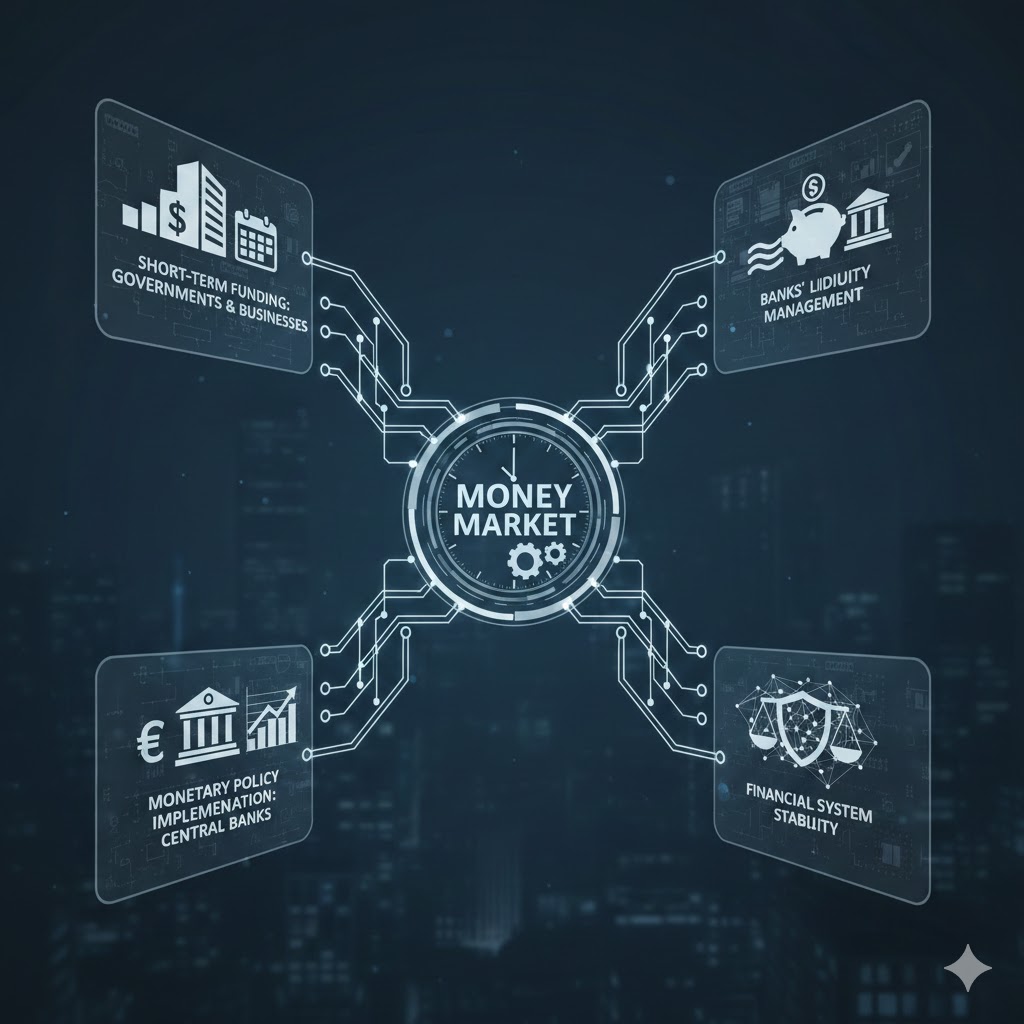
In short, the money market keeps the financial system running smoothly by ensuring that cash is available where and when it’s needed.
Leave a comment