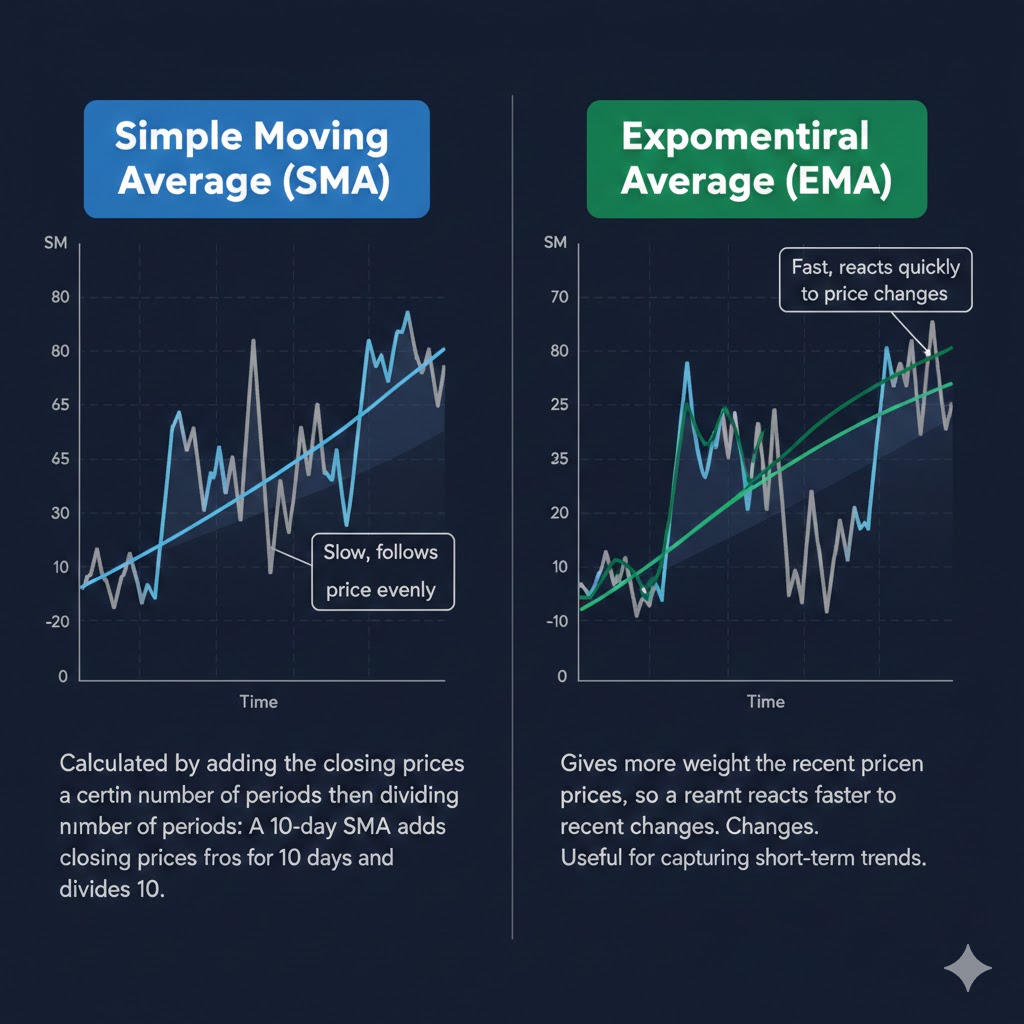
The Moving Average is the average of a selected range of prices, usually closing prices, over a specific number of periods (e.g., days, hours).
Purpose: To highlight the trend direction by smoothing price data.
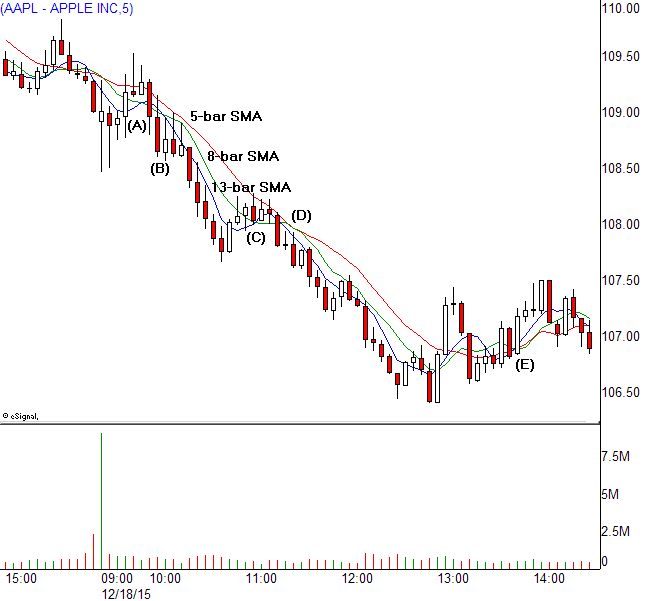
Common Moving Average Periods (in days)
- Short-term MAs:
- 5-day, 10-day, 14-day
- Used for quick, responsive trend signals
- Useful for day trading or short-term swing trading
- Medium-term MAs:
- 20-day, 50-day
- Often used to identify intermediate trends
- Popular among swing traders and position traders
- Long-term MAs:
- 100-day, 200-day
- Used to spot long-term trend direction
- Very common for investors and longer-term traders
Types of Moving Averages
How Moving Averages Are Used
- Trend Identification:
- When price is above the MA, the trend is usually considered up.
- When price is below the MA, the trend is usually considered down.
- Support and Resistance:
- MAs can act as dynamic support or resistance levels.
- Crossovers:
- When a short-term MA crosses above a long-term MA, it can signal a potential buy (bullish crossover).
- When it crosses below, it may signal a sell (bearish crossover).
How to Choose the Number of Days?
- Shorter MA (e.g., 5 or 10 days): More sensitive to price changes but more prone to false signals.
- Longer MA (e.g., 100 or 200 days): Smoother and better for filtering out noise, but slower to react.