Legal factors refer to the laws and regulations that a business must comply with in the countries or regions it operates. These factors are crucial because they set the legal framework within which businesses must function, and non-compliance can lead to fines, legal actions, or damage to reputation.
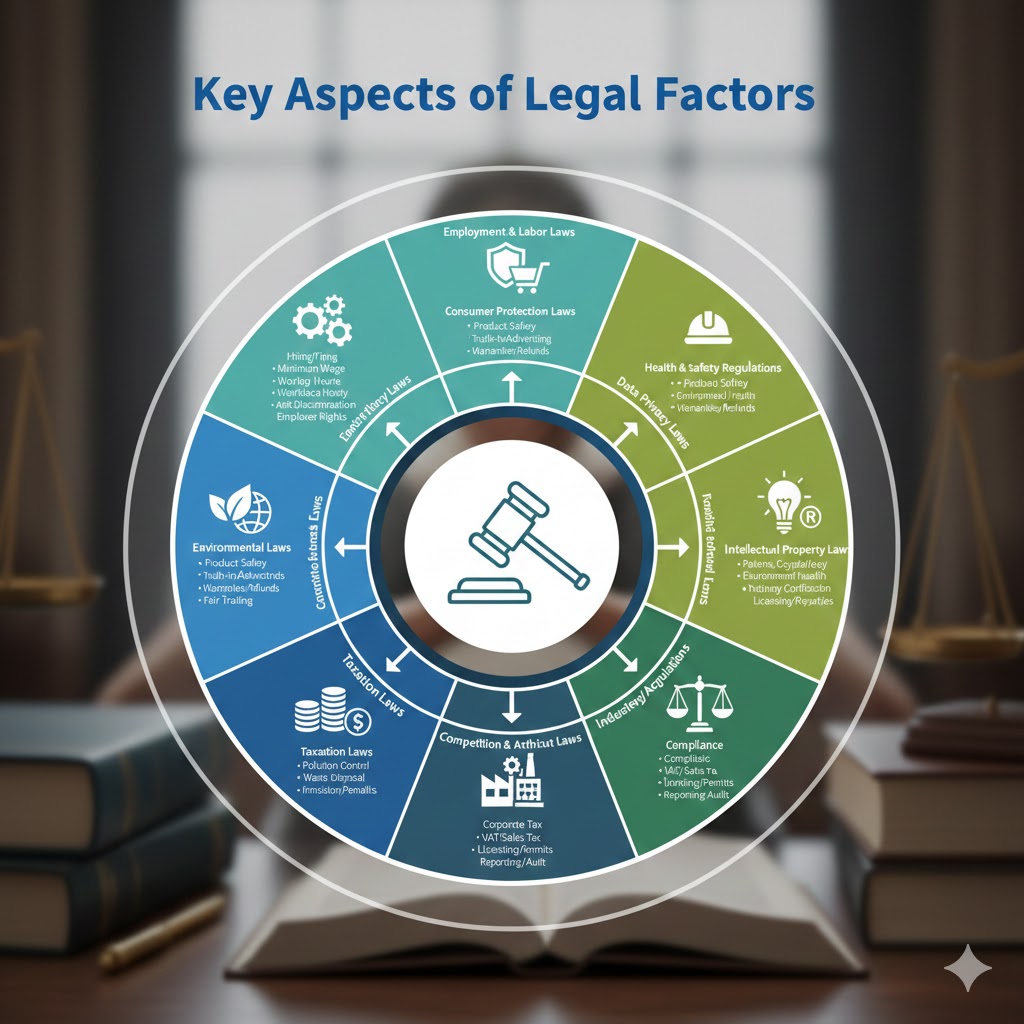
Key Aspects of Legal Factors:
- Employment and Labor Laws
- Regulations on hiring and firing
- Minimum wage laws
- Working hours and overtime rules
- Workplace safety and health standards
- Anti-discrimination laws
- Employee rights and benefits
- Consumer Protection Laws
- Product safety standards
- Truth-in-advertising regulations
- Privacy and data protection laws (e.g., GDPR)
- Warranties and refunds policies
- Fair trading laws
- Health and Safety Regulations
- Occupational safety requirements
- Environmental health standards
- Industry-specific safety protocols
- Mandatory training and certification
- Intellectual Property Laws
- Patents, copyrights, trademarks protection
- Protection against infringement and piracy
- Licensing and royalties regulations
- Competition and Antitrust Laws
- Rules to prevent monopolies and promote fair competition
- Regulations against price fixing, collusion, or abuse of market power
- Mergers and acquisitions controls
- Industry-Specific Regulations
- Compliance requirements for sectors like finance, healthcare, food, pharmaceuticals, telecommunications, and transportation
- Licensing and permits
- Reporting and audit obligations
- Taxation Laws
- Corporate tax obligations
- VAT and sales tax regulations
- Tax incentives or penalties
- Environmental Laws
- Compliance with pollution control laws
- Waste disposal regulations
- Emission limits and sustainability mandates
Why Legal Factors Matter
- They protect businesses and consumers by setting clear rules.
- They influence business costs through compliance expenses.
- They affect operational flexibility and strategic choices.
- They can create barriers to entry or competitive advantages.
- Non-compliance can lead to legal penalties, lawsuits, and reputational damage.