Behavioural Finance is a field of study that combines psychology and finance to understand how emotions, cognitive biases, and social factors influence investors’ decisions and financial markets.
Key Points:
- Unlike traditional finance, which assumes investors are fully rational, behavioural finance acknowledges that people often make irrational decisions.
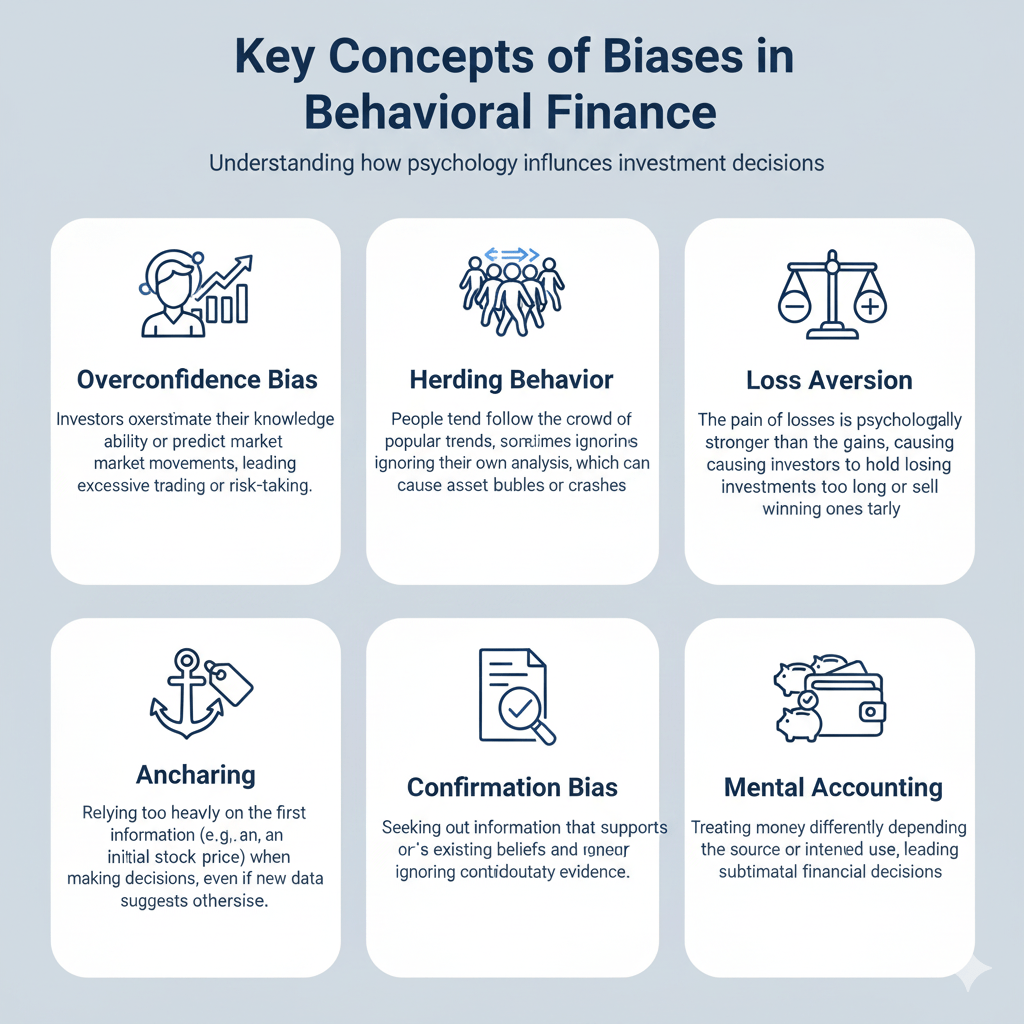
- It studies common biases such as overconfidence, herding behavior, loss aversion, and confirmation bias.
- These biases can lead to market anomalies like bubbles, crashes, and mispricing of assets.
- Understanding behavioural finance helps investors and financial professionals recognize and mitigate emotional and cognitive errors in decision-making.
Impacts on Financial Markets
- Market bubbles and crashes often result from collective irrational behaviour driven by biases.
- Asset prices may deviate from their true value because of emotional trading.
- Investors’ decisions are influenced by mood, social pressures, and cognitive shortcuts rather than purely rational analysis.
Practical Applications
- Investment Strategies: Incorporating behavioural insights to improve decision-making and portfolio management.
- Risk Management: Recognizing biases helps in avoiding excessive risk-taking or panic selling.
- Financial Education: Teaching investors about common biases to foster better habits.
- Market Regulation: Regulators use behavioural finance to design policies protecting investors.
Summary
Behavioural Finance bridges the gap between psychology and economics, explaining why markets are not always efficient and why investor behaviour often deviates from rational models. Understanding these concepts can lead to smarter investing and better financial outcomes.